Vegetable Shortening
What is Vegetable Shortening?
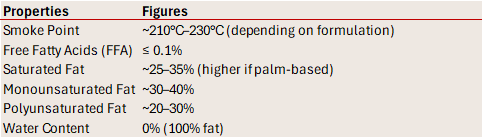
Vegetable shortening is a semi-solid fat made from refined vegetable oils, most commonly palm oil, soybean oil, or cottonseed oil, which have been hydrogenated to create a firm, white fat that is solid at room temperature. Unlike butter or margarine, shortening contains no water or milk solids—making it 100% fat.
Shortening is primarily used in baking and deep-frying due to its unique ability to produce tender, flaky textures in pie crusts, cookies, pastries, and biscuits. It also offers exceptional stability under high heat, with a long shelf life and resistance to rancidity, which makes it ideal for high-turnover food production environments.
It is called "shortening" because it interferes with gluten formation in doughs, "shortening" the strands to create a crumbly or flaky texture.
Vegetable Shortening Properties
Shortening is neutral in flavor, does not require refrigeration, and offers extended frying life, especially in commercial operations. Modern versions are often trans fat–free, using interesterified or palm-based blends instead of partially hydrogenated oils. It is a staple in bakeries, fast food chains, and large-scale food manufacturing.